Parmesan cheese nutrition facts are often searched by people who want to understand how this widely consumed aged cheese fits into everyday eating habits.
Since Parmesan is usually eaten in small amounts, its nutritional value is best viewed in terms of nutrient concentration rather than serving size alone.
Many individuals are interested in how Parmesan’s composition relates to broader dietary goals, such as protein intake, mineral balance, and sodium awareness.
Gaining a clear understanding of its nutritional characteristics can help place Parmesan cheese appropriately within a balanced diet, especially for those following specific eating patterns or paying closer attention to their overall nutrient intake.
What Is Parmesan Cheese?
Parmesan cheese is a hard, aged cheese produced from cow’s milk using controlled fermentation and extended maturation.
The traditional and legally protected version, Parmigiano-Reggiano, is made in designated regions of Italy under defined production standards.
Outside these regions, Parmesan-style cheeses are manufactured using comparable methods, though aging duration and flavor intensity may vary.
The defining features of Parmesan cheese include its firm, granular texture and pronounced savory taste, both of which develop during the aging process.
These characteristics distinguish it from softer cheeses and contribute to its widespread culinary use and nutritional concentration.
Parmesan Cheese Nutrition Facts
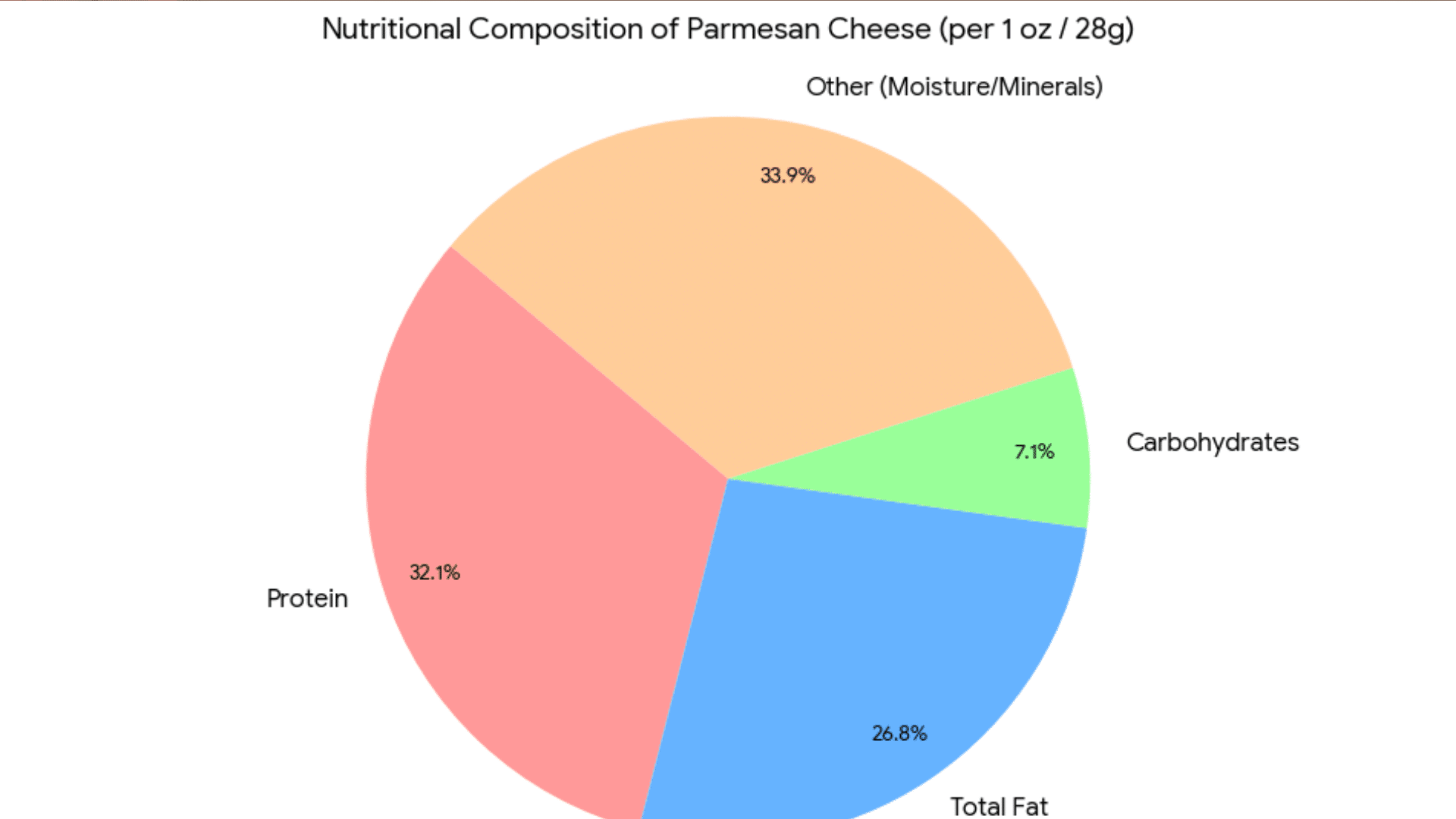
Parmesan cheese provides a concentrated source of essential nutrients due to its aging process, making small portions nutritionally significant within a balanced diet.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 oz (28 g) |
| Calories | 110–120 kcal |
| Protein | 8–10 g |
| Total Fat | 7–8 g |
| Saturated Fat | 4–5 g |
| Carbohydrates | 1–3 g |
| Sugars | 0 g |
| Calcium | 240–330 mg |
| Phosphorus | ~200 mg |
| Sodium | 400–500 mg |
| Cholesterol | 20–25 mg |
When consumed in moderation, Parmesan cheese can contribute protein and key minerals while fitting appropriately into a variety of dietary patterns.
How Parmesan Cheese Is Made (Process)
Parmesan cheese is produced through a traditional, carefully controlled process that focuses on natural fermentation, moisture reduction, and long-term aging.
- Milk selection: Fresh cow’s milk is chosen to achieve the proper balance of fat and protein.
- Curd formation: Starter cultures and rennet are added, allowing the milk to coagulate and form curds.
- Cutting and cooking: Curds are finely cut and gently heated to remove excess moisture.
- Molding and pressing: The curds are placed into round molds and pressed into large wheels.
- Salting: Cheese wheels are soaked in a salt brine to boost flavor and preservation.
- Aging: The cheese is aged for 12 to 36 months or longer to develop its firm texture and rich flavor.
This extended process gives Parmesan cheese its distinctive taste, structure, and concentrated nutritional qualities.
Interesting Fact You Should KnowParmesan cheese is considered nutrient-dense because even small amounts provide concentrated micronutrients. It is especially rich in calcium and phosphorus for bone strength, vitamin B12 for nerve and blood health, and zinc for immune function, primarily due to its long aging process. |
Health Benefits of Parmesan Cheese
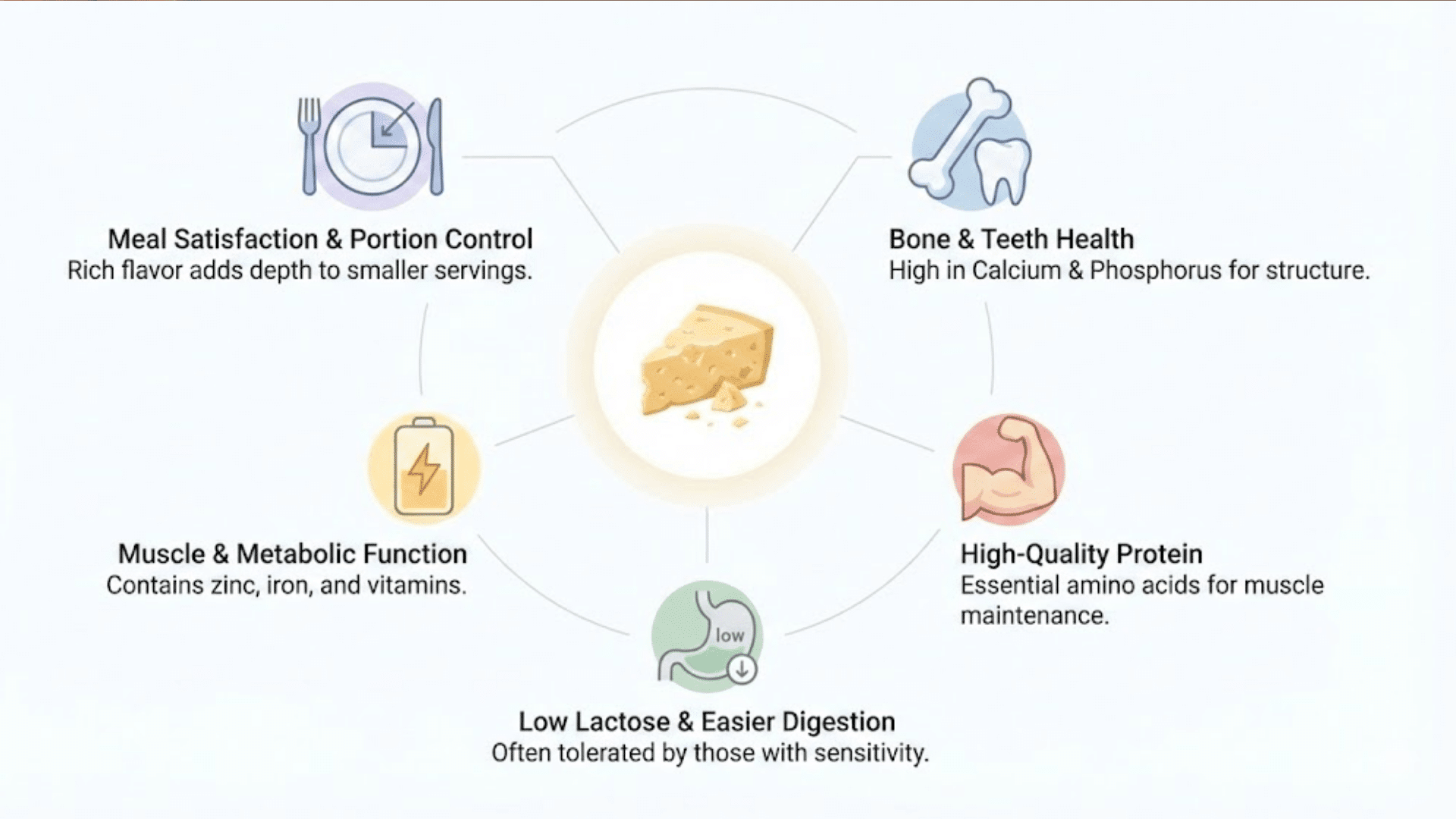
Parmesan cheese provides several health benefits when eaten in moderation, mainly due to its nutrient concentration and aging process.
1. Supports Bone and Teeth Health
Parmesan cheese supplies calcium and phosphorus, minerals that are essential for maintaining bone strength, supporting tooth structure, and reducing the risk of bone mineral loss over time.
2. Provides High-Quality Protein
Parmesan contains complete protein with all essential amino acids, which helps support muscle maintenance, tissue repair, and satiety as part of a balanced diet.
3. Naturally Low in Lactose
The long aging process breaks down most of the lactose in Parmesan cheese, making it easier to digest for many individuals with lactose intolerance.
4. Supports Muscle and Metabolic Function
Parmesan provides protein along with B vitamins and minerals that contribute to normal muscle function and energy metabolism at the cellular level.
5. Helps Promote Meal Satisfaction
The strong savory flavor of Parmesan allows small amounts to add depth to meals, which may help with portion control and overall calorie awareness.
Best Ways to Use Parmesan Cheese (Practical and Healthy)
Parmesan cheese can be included in meals in simple, mindful ways that add flavor and nutrition without significantly increasing calories or sodium.
- Use as a finishing touch: Add a small sprinkle over pasta, soups, or vegetables just before serving for maximum flavor.
- Pair with vegetables: Combine Parmesan with roasted or steamed vegetables to improve taste and encourage balanced meals.
- Add to protein dishes: Use Parmesan in eggs, lean meats, or grain bowls to complement other protein sources.
- Replace heavy sauces: Choose Parmesan instead of creamy sauces to add richness while keeping meals lighter.
- Measure portions: Use measured amounts, as small servings provide strong flavor and help maintain portion control.
Using Parmesan strategically allows its taste and nutrients to enhance meals while supporting balanced, health-conscious eating.
Downsides of Parmesan Cheese
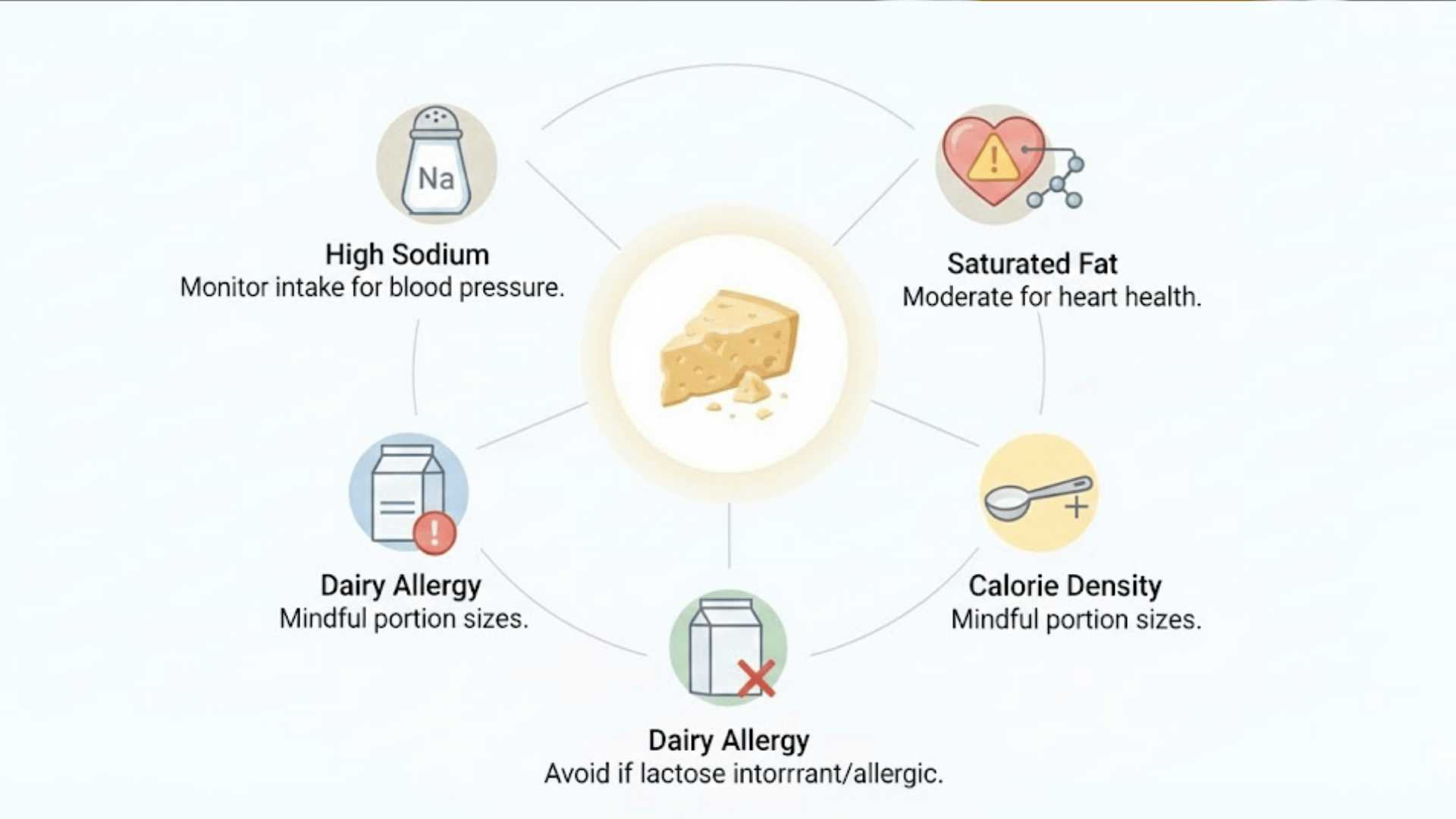
Although Parmesan cheese offers nutritional benefits, certain factors should be considered to ensure it fits safely within a balanced diet.
- High sodium content: Parmesan contains significant sodium, which may be a concern for individuals managing blood pressure or salt intake.
- Saturated fat levels: The cheese provides saturated fat, which should be consumed in moderation as part of heart-conscious eating patterns.
- Calorie density: Small portions are recommended, as Parmesan is energy-dense despite its compact serving size.
- Not suitable for dairy allergies: Individuals with milk protein allergies should avoid Parmesan cheese entirely.
- Possible digestive sensitivity: Some people may still experience discomfort despite its low lactose content.
Mindful portioning and individual dietary needs are key to enjoying Parmesan cheese while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Is Parmesan Cheese Healthy?
Parmesan cheese can be a healthy addition to a balanced diet when eaten in moderation.
It provides high-quality protein and essential minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which support bone strength and normal muscle function.
Because Parmesan is aged for extended periods, its lactose content is very low, making it easier to digest for many people with lactose sensitivity.
Its rich, savory flavor also allows smaller portions to enhance meals without excessive calorie intake.
However, Parmesan is relatively high in sodium and saturated fat, so mindful portion control is essential, especially for individuals monitoring heart health or blood pressure.
When used thoughtfully, Parmesan cheese can contribute valuable nutrients while fitting well into overall healthy eating patterns.
Final Thoughts
Understanding Parmesan cheese nutrition facts helps place this aged cheese into a balanced and practical eating approach.
Its concentrated flavor and nutrient density make it easy to use in small amounts while still adding depth to meals.
When paired with whole, nutrient-rich foods and consumed mindfully, Parmesan can complement a variety of dietary patterns.
Paying attention to portion size and individual nutrition needs allows this cheese to be enjoyed without excess.
With informed choices and moderation, Parmesan cheese can remain a flavorful and thoughtful addition to everyday meals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Aging Time Change Parmesan’s Nutrition?
Longer aging reduces moisture, which concentrates nutrients, flavor, and sodium per gram of cheese.
Is Block Parmesan Healthier Than Pre-Grated Parmesan?
Block Parmesan usually contains fewer additives and offers a purer ingredient profile.
Can Parmesan Cheese Fit Into a Diabetic Diet?
Yes, when eaten in small portions alongside balanced meals with fiber and protein.
Is It Safe to Eat Parmesan Cheese Daily?
Small daily amounts are generally safe if overall sodium and fat intake remain balanced.